15/2/22
Copied from another thread, relevant to be compiled in this thread for ease of future accessibility and learning.
Question asked by
@TheFunkMachine #2,478
Do BrainChip patents cover a wide spectrum in the digital SNN of neuromorphic chips while others could potentially go down the less beneficial route of analogue SNN to get around BrainChip patents?
Answered by
@Diogenese #2,525
The scope of protection of a patent is determined by how the invention is defined in the patent claims. To avoid infringement, a competitor would need to design a digital neuron which does not fall within the definition of our invention as set out in the patent claims.
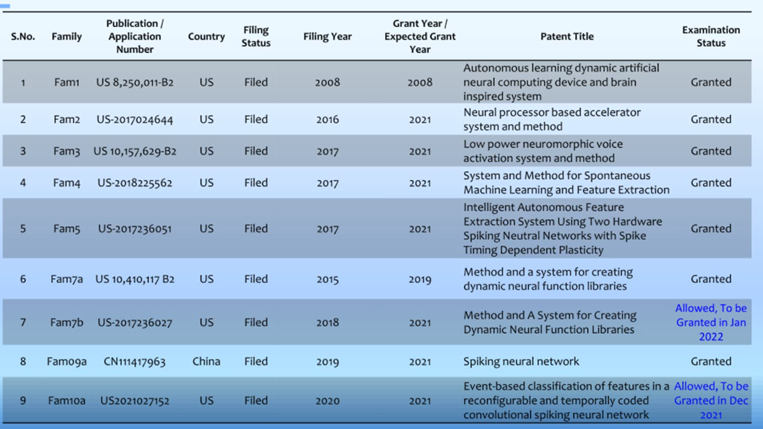
The earliest BrainChip patent US8250011 and its continuation US11238342 date from 21 September 2008 and protect a digital neuron.
US8250011B2 Autonomous learning dynamic artificial neural computing device and brain inspired system
US11238342B2 Method and a system for creating dynamic neural function libraries
https://brainchipinc.com/brainchip-...-learned-functions-intelligent-target-device/
Key features of Patent US 11,238,342
- The patent claims protect the basic structure and function of a digital neuron consisting of multiple synapse circuits connected to a soma circuit in analogy to a biological neuron where a soma (i.e. neuron) cell receives its inputs via multiple synapses.
This patent is a continuation of previous BrainChip patents US 8,250,011 and US 10,410,117, protecting features previously disclosed but not previously claimed. The title of this patent has been inherited from US 10,410,117 but would be better represented by the title of US 8,250,011 “Autonomous Learning Dynamic Artificial Neural Computing Device and Brain Inspired System.”
The main claim of US8250011:
1. An information processing system intended for use in artificial intelligence and having
a plurality of digital artificial neuron circuits connected in an array, the system comprising
a plurality of digital dynamic synapse circuits, wherein each digital dynamic synapse circuit contains
a binary register that stores a value representing neurotransmitter type and level, wherein the digital dynamic synapse circuits comprise
a means of learning and responding to input signals, either by producing or compounding the value, thereby simulating behavior of a biological synapse; and
a temporal integrator circuit that integrates and combines each individually simulated synapse neurotransmitter type and value over time, wherein time is dependent on the neurotransmitter type stored in each digital dynamic synapse circuit.
The main claim of US11238342:
1. A neural network apparatus, comprising:
a soma circuit;
a plurality of digital dynamic synapse circuits connected to the soma circuit, wherein each of the plurality of digital dynamic synapse circuits includes a
respective binary register, and wherein each binary register is
configured to store a strength value representing a neurotransmitter type and a level; and
a post synaptic potential (PSP) circuit included within a respective digital dynamic synapse circuit, the PSP circuit
producing a PSP value in each digital dynamic synapse circuit in response to receipt of an input pulse, the PSP value being a sum of the strength value and a then-current-decremented PSP value, and
a temporal integrator circuit configured to integrate and combine each of the PSP values over time, producing a membrane potential value.
These claims are directed to protection of a digital neuron.
Other features, such as Machine Learning are protected by other patents.
(
US11151441B2 System and method for spontaneous machine learning and feature extraction, 8 Feb 2017) (
This may be used for "Hey Mercedes!")
1. A digital system for spontaneous machine learning and feature extraction, the system comprising:
digital hardware circuitry that includes a hierarchical arrangement of a
first artificial neural network and a second artificial neural network, wherein
the first artificial neural network spontaneously learns to recognize any repeating patterns in an input stream and
the second artificial neural network is trained to interpret and label the repeating patterns recognized by the first artificial neural network,
wherein the first artificial neural network includes
- a plurality of digital neuron circuits,
- a plurality of digital synapse circuits, and
- an address event representation (AER) bus,
the first artificial neural network being connected to the input stream via the AER bus, the input stream comprising temporally and spatially distributed spikes encoded on the AER bus;
wherein
the first artificial neural network transmits spikes to the second artificial neural network, the spikes representing the recognized repeating patterns learned from the input stream; and
wherein the plurality of digital neuron circuits are interconnected using the plurality of digital synapse circuits, and wherein
interconnectivity and strength of the plurality of digital synapse circuits are configurable through digital registers that are externally accessed.