uiux
Regular
Brainchip + PROPHESEE + RTX
This combination of companies give us a Neuromorphic Processor, a Neuromorphic Vision Sensor and a very large defence contractor with multiple uses for the aforementioned combination of technologies.....

Courtesy of @Quiltman

Courtesy of @Frangipani

Courtesy of @chapman89
Sensors Unlimited Patents
Originally founded in 1991 as a research and development company, Sensors Unlimited, Inc. became a leading supplier of InGaAs technology and shortwave IR imaging solutions. Now part of Raytheon, an RTX Business, the company operates a 97,000-square-foot ISO 9001:2015 certified facility, featuring a III-V foundry with Class 100 clean rooms. Their proprietary InGaAs platform supports SWIR cameras, focal plane arrays (FPAs), and extended wavelength sensors for applications like laser tracking, surveillance, unmanned vehicle payloads, night vision, and free-space communications. With over 75 years of combined experience, the team provides custom-designed imaging solutions for aerospace, defense, security, and industrial applications, delivering cutting-edge technology to safeguard national and global security.
US20240292074 - NEUROMORPHIC COMPRESSIVE SENSING IN LOW-LIGHT ENVIRONMENT
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=US437770982
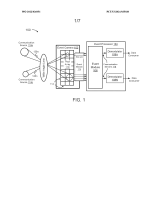
This patent describes a Neuromorphic Vision (NMV) System that improves image reconstruction in low-light environments by using neuromorphic vision sensors and processors. Unlike conventional CMOS sensors, which struggle with sensitivity limits and saturation, NMV sensors accumulate light over time and fire an event when a threshold is reached. This event-based approach ensures that no light information is lost, making NMV sensors ideal for military surveillance, autonomous navigation, and security systems. The NMV processor receives these event signals, timestamps them, and processes them into spatiotemporal spike patterns (SSPs). These patterns are then used by a compressive sensing and reconstruction (CSR) engine, which converts them into high-quality images or videos. This method enables efficient low-light imaging with reduced energy consumption, simplified hardware, and enhanced robustness against noise.

This diagram illustrates a Neuromorphic Vision (NMV) System for low-light imaging, showing how NMV sensors capture and process visual information. A scene under low-light conditions is observed by an NMV sensor array, where each sensor accumulates light and fires an event when a threshold is reached. These event signals are sent to an NMV processor, which timestamps and organizes them into spatiotemporal spike patterns (SSPs). This event-based approach prevents information loss, reduces power consumption, and enables compressive sensing-based image reconstruction, making it ideal for surveillance, autonomous navigation, and military applications.
US20210105421 - Neuromorphic vision with frame-rate imaging for target detection and tracking
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=US321528812
This patent describes an imaging system that integrates neuromorphic vision sensors and neuromorphic processors to enhance target detection and tracking in real-world surveillance and reconnaissance applications. Traditional frame-rate imaging systems provide high spatial resolution but consume excessive power, bandwidth, and memory due to continuous frame capture. In contrast, neuromorphic vision sensors operate asynchronously, detecting pixel-level changes only when motion occurs, providing high temporal resolution with minimal data output.
The system incorporates an infrared focal plane array (FPA) for capturing detailed intensity images alongside neuromorphic vision sensors that detect motion in real time. A read-out integrated circuit (ROIC) processes both intensity images and neuromorphic event data. A key feature is the adaptive frame-rate control, where the neuromorphic processors analyze event-based data, triggering an increase in frame rate only when necessary, significantly reducing unnecessary data processing.
A fused algorithm module, powered by neuromorphic processors, employs machine learning to correlate event-based neuromorphic vision sensor data with frame-based intensity images. This combination enhances object detection, tracking, and scene reconstruction, even in environments with background clutter, occlusion, or high-altitude surveillance. By leveraging neuromorphic vision sensors and neuromorphic processors, the system provides a scalable, power-efficient, and high-speed imaging solution for applications such as autonomous navigation, military ISR, and aerial surveillance.


This image illustrates a surveillance and reconnaissance system utilizing neuromorphic vision sensors and neuromorphic processors for real-time target detection and tracking. A satellite (100) is shown monitoring various military assets, including aircraft, ships, and ground installations, by capturing and analyzing event-based visual data. The satellite is equipped with neuromorphic vision sensors, which passively detect motion and changes in the scene with high temporal resolution, reducing the need for constant frame capture. The data is processed onboard using neuromorphic processors, which enable real-time event detection, reducing bandwidth usage and improving response times. This system is designed for high-altitude intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR), providing efficient, low-power, and adaptive tracking of fast-moving targets.
RTX Patents
US20240365014 - OBJECT RECONSTRUCTION WITH NEUROMORPHIC SENSORS
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=US441933492
This patent describes a neuromorphic vision-based 3D reconstruction system that leverages neuromorphic cameras and neuromorphic processors to generate high-fidelity images of dynamic scenes. Unlike traditional methods that rely on multi-view RGB images and struggle with moving objects, this system uses event-based neuromorphic vision sensors to capture asynchronous event data with high temporal resolution. The process involves aligning unaligned event data in time, generating event volumes, and processing them using a Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) model to reconstruct high-quality 3D images or scenes. The system reduces motion blur, enhances object tracking, and improves rendering of dynamic environments by integrating neuromorphic image processing techniques with machine learning. Applications include ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance), robotics, autonomous systems, and industrial automation, where real-time 3D scene understanding is crucial.

This diagram (FIG. 3) illustrates a neuromorphic vision-based 3D reconstruction process for a very fast-moving object (a jet) using neuromorphic vision sensors and neuromorphic processors. Multiple event cameras (labeled Event Camera 1 through Event Camera N) capture asynchronous event data from different viewpoints, generating multiview event volumes (304), which represent the scene in a planar format. These event volumes are processed to infer learned poses (306), which help reconstruct the object's spatial orientation and movement. Finally, using a neural radiance field (NeRF) model, the system synthesizes high-fidelity 3D object reconstructions (308A, 308B) with improved accuracy. This approach leverages neuromorphic imaging to handle rapid motion and reduce motion blur, making it ideal for autonomous systems, defense applications, and ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance) tasks.
One of the listed inventors is Ganesh Sundaramoorthi and on his website you can see a reference to BrainChip:
http://ganeshsun.com/
WO2022026051 - SYSTEMS, DEVICES, AND METHODS FOR OPTICAL COMMUNICATION
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2022026051
This patent describes an optical communication system that utilizes neuromorphic vision sensors and neuromorphic processors to enhance free-space optical (FSO) communication. The system employs an event camera, also called a neuromorphic camera, to receive optically transmitted signals. Unlike traditional cameras, neuromorphic vision sensors capture data asynchronously by detecting changes in brightness at the pixel level, significantly improving response time and power efficiency.
The event camera generates an event stream consisting of timestamps and pixel addresses for detected light variations. A neuromorphic processor then demultiplexes this event stream into multiple communication streams, each corresponding to a different optical signal source, such as satellites, UAVs, or ground stations. The processor filters out noise, reconstructs optical signals, and passes them to a demodulator that extracts transmitted data.
The patent also describes how the system tracks moving optical sources (e.g., satellites or aircraft) by analyzing changes in received light paths. Using this method, the system can estimate the 3D position of communication sources, identify trusted senders, and reject unverified transmissions. This capability makes it highly effective for secure satellite networks, defense applications, and high-speed optical data transfer.
By leveraging neuromorphic vision sensors and neuromorphic processors, this system enables fast, low-latency optical communication, improving the robustness and security of satellite-to-satellite and satellite-to-ground links. The approach is particularly advantageous for autonomous tracking, space-based mesh networks, and high-speed optical data relays in dynamic environments.


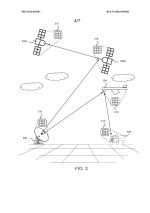
This diagram (FIG. 3) illustrates a free-space optical (FSO) communication network utilizing neuromorphic vision sensors and neuromorphic processors for high-speed optical data transmission. The system consists of multiple communication nodes, including satellites (302a, 302b), a ground station (306), an aerial platform (304), and a vehicle-based receiver (308).
Each of these nodes is equipped with an optical communication system (310) that includes neuromorphic cameras for detecting and processing optical signals. The diagram demonstrates how optical signals are exchanged between satellites and ground-based receivers, forming a space-based optical mesh network. The neuromorphic vision sensors in the system enable real-time processing of light signals by detecting changes in brightness at high speeds, reducing latency and improving communication reliability.
This system is designed for secure, high-bandwidth, low-latency optical communications, particularly for applications in satellite networks, aerospace, defense, and autonomous vehicle communication.
US20210348966 - Systems, devices, and methods for hyperspectral imaging
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=US341179803
This patent describes a hyperspectral imaging system that integrates neuromorphic vision sensors with an interferometer to capture and process spectral data in real-time across visible and non-visible wavelengths (e.g., infrared and ultraviolet). The system uses an event-based neuromorphic camera, which detects brightness changes asynchronously at each pixel, significantly reducing data redundancy and improving response time compared to conventional imaging. Light from an interferometer, such as a Translating Wedge-Based Identical Pulses Encoding System (TWINS), is processed by a neuromorphic processor that applies digital demodulation and a Non-Uniform Discrete Cosine Transform (NDCT) to extract spectral information. This enables the generation of hyperspectral images with precise spectral resolution, suitable for military surveillance, medical diagnostics, remote sensing, and security applications. The system also includes a calibration laser for spectral accuracy and adaptive processing that dynamically adjusts spectral bands in response to real-time conditions. By leveraging neuromorphic processors and neuromorphic vision sensors, this technology provides high-speed, low-latency spectral analysis with enhanced sensitivity in low-light environments, making it ideal for applications requiring real-time hyperspectral imaging and advanced object detection.

This diagram illustrates a hyperspectral imaging system that integrates an interferometer, neuromorphic vision sensor, and event-based processing for real-time spectral analysis. Light from an input scene passes through a Translating-Wedge-Based Identical Pulses Encoding System (TWINS) interferometer, modulated by a resonant actuator and calibrated using a laser source. The processed light is captured by a neuromorphic event camera, which detects brightness changes asynchronously and outputs an event stream instead of conventional frames. This stream is processed by a neuromorphic processor that applies digital demodulation and frequency transforms to extract spectral data, generating hyperspectral images with enhanced resolution and sensitivity, ideal for applications like remote sensing, medical imaging, and defense.
ChatGPT description of these individual components forming part of a missile defense system:
This system would be an advanced real-time detection, tracking, and interception network designed to counter hypersonic missiles, stealth aircraft, and other high-speed threats. It combines neuromorphic vision sensors, hyperspectral imaging, optical communication, and AI-powered 3D reconstruction to create a fast, power-efficient, and highly adaptive defense system.
How It Works:
Detection & Early Warning
Tracking High-Speed Threats:
Interception & Countermeasures:
Why It’s a Game-Changer:
This combination of companies give us a Neuromorphic Processor, a Neuromorphic Vision Sensor and a very large defence contractor with multiple uses for the aforementioned combination of technologies.....
Courtesy of @Quiltman
Courtesy of @Frangipani
Courtesy of @chapman89
Sensors Unlimited Patents
Originally founded in 1991 as a research and development company, Sensors Unlimited, Inc. became a leading supplier of InGaAs technology and shortwave IR imaging solutions. Now part of Raytheon, an RTX Business, the company operates a 97,000-square-foot ISO 9001:2015 certified facility, featuring a III-V foundry with Class 100 clean rooms. Their proprietary InGaAs platform supports SWIR cameras, focal plane arrays (FPAs), and extended wavelength sensors for applications like laser tracking, surveillance, unmanned vehicle payloads, night vision, and free-space communications. With over 75 years of combined experience, the team provides custom-designed imaging solutions for aerospace, defense, security, and industrial applications, delivering cutting-edge technology to safeguard national and global security.
US20240292074 - NEUROMORPHIC COMPRESSIVE SENSING IN LOW-LIGHT ENVIRONMENT
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=US437770982
This patent describes a Neuromorphic Vision (NMV) System that improves image reconstruction in low-light environments by using neuromorphic vision sensors and processors. Unlike conventional CMOS sensors, which struggle with sensitivity limits and saturation, NMV sensors accumulate light over time and fire an event when a threshold is reached. This event-based approach ensures that no light information is lost, making NMV sensors ideal for military surveillance, autonomous navigation, and security systems. The NMV processor receives these event signals, timestamps them, and processes them into spatiotemporal spike patterns (SSPs). These patterns are then used by a compressive sensing and reconstruction (CSR) engine, which converts them into high-quality images or videos. This method enables efficient low-light imaging with reduced energy consumption, simplified hardware, and enhanced robustness against noise.
This diagram illustrates a Neuromorphic Vision (NMV) System for low-light imaging, showing how NMV sensors capture and process visual information. A scene under low-light conditions is observed by an NMV sensor array, where each sensor accumulates light and fires an event when a threshold is reached. These event signals are sent to an NMV processor, which timestamps and organizes them into spatiotemporal spike patterns (SSPs). This event-based approach prevents information loss, reduces power consumption, and enables compressive sensing-based image reconstruction, making it ideal for surveillance, autonomous navigation, and military applications.
US20210105421 - Neuromorphic vision with frame-rate imaging for target detection and tracking
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=US321528812
This patent describes an imaging system that integrates neuromorphic vision sensors and neuromorphic processors to enhance target detection and tracking in real-world surveillance and reconnaissance applications. Traditional frame-rate imaging systems provide high spatial resolution but consume excessive power, bandwidth, and memory due to continuous frame capture. In contrast, neuromorphic vision sensors operate asynchronously, detecting pixel-level changes only when motion occurs, providing high temporal resolution with minimal data output.
The system incorporates an infrared focal plane array (FPA) for capturing detailed intensity images alongside neuromorphic vision sensors that detect motion in real time. A read-out integrated circuit (ROIC) processes both intensity images and neuromorphic event data. A key feature is the adaptive frame-rate control, where the neuromorphic processors analyze event-based data, triggering an increase in frame rate only when necessary, significantly reducing unnecessary data processing.
A fused algorithm module, powered by neuromorphic processors, employs machine learning to correlate event-based neuromorphic vision sensor data with frame-based intensity images. This combination enhances object detection, tracking, and scene reconstruction, even in environments with background clutter, occlusion, or high-altitude surveillance. By leveraging neuromorphic vision sensors and neuromorphic processors, the system provides a scalable, power-efficient, and high-speed imaging solution for applications such as autonomous navigation, military ISR, and aerial surveillance.
This image illustrates a surveillance and reconnaissance system utilizing neuromorphic vision sensors and neuromorphic processors for real-time target detection and tracking. A satellite (100) is shown monitoring various military assets, including aircraft, ships, and ground installations, by capturing and analyzing event-based visual data. The satellite is equipped with neuromorphic vision sensors, which passively detect motion and changes in the scene with high temporal resolution, reducing the need for constant frame capture. The data is processed onboard using neuromorphic processors, which enable real-time event detection, reducing bandwidth usage and improving response times. This system is designed for high-altitude intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR), providing efficient, low-power, and adaptive tracking of fast-moving targets.
RTX Patents
US20240365014 - OBJECT RECONSTRUCTION WITH NEUROMORPHIC SENSORS
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=US441933492
This patent describes a neuromorphic vision-based 3D reconstruction system that leverages neuromorphic cameras and neuromorphic processors to generate high-fidelity images of dynamic scenes. Unlike traditional methods that rely on multi-view RGB images and struggle with moving objects, this system uses event-based neuromorphic vision sensors to capture asynchronous event data with high temporal resolution. The process involves aligning unaligned event data in time, generating event volumes, and processing them using a Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) model to reconstruct high-quality 3D images or scenes. The system reduces motion blur, enhances object tracking, and improves rendering of dynamic environments by integrating neuromorphic image processing techniques with machine learning. Applications include ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance), robotics, autonomous systems, and industrial automation, where real-time 3D scene understanding is crucial.
This diagram (FIG. 3) illustrates a neuromorphic vision-based 3D reconstruction process for a very fast-moving object (a jet) using neuromorphic vision sensors and neuromorphic processors. Multiple event cameras (labeled Event Camera 1 through Event Camera N) capture asynchronous event data from different viewpoints, generating multiview event volumes (304), which represent the scene in a planar format. These event volumes are processed to infer learned poses (306), which help reconstruct the object's spatial orientation and movement. Finally, using a neural radiance field (NeRF) model, the system synthesizes high-fidelity 3D object reconstructions (308A, 308B) with improved accuracy. This approach leverages neuromorphic imaging to handle rapid motion and reduce motion blur, making it ideal for autonomous systems, defense applications, and ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance) tasks.
One of the listed inventors is Ganesh Sundaramoorthi and on his website you can see a reference to BrainChip:
http://ganeshsun.com/
Organized a workshop at Raytheon Technolgies on Event-Based Sensing, Algorithms, and Processing Hardware across industry (e.g., Raytheon, Intel, Brainchip), governement (e.g., DARPA, AirForce, SpaceForce) and academia (e.g., Georgia Tech, Purdue, UPenn, UIUC, U. Maryland). Excited for the future of neuromorphic computing in advancing AI!
WO2022026051 - SYSTEMS, DEVICES, AND METHODS FOR OPTICAL COMMUNICATION
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2022026051
This patent describes an optical communication system that utilizes neuromorphic vision sensors and neuromorphic processors to enhance free-space optical (FSO) communication. The system employs an event camera, also called a neuromorphic camera, to receive optically transmitted signals. Unlike traditional cameras, neuromorphic vision sensors capture data asynchronously by detecting changes in brightness at the pixel level, significantly improving response time and power efficiency.
The event camera generates an event stream consisting of timestamps and pixel addresses for detected light variations. A neuromorphic processor then demultiplexes this event stream into multiple communication streams, each corresponding to a different optical signal source, such as satellites, UAVs, or ground stations. The processor filters out noise, reconstructs optical signals, and passes them to a demodulator that extracts transmitted data.
The patent also describes how the system tracks moving optical sources (e.g., satellites or aircraft) by analyzing changes in received light paths. Using this method, the system can estimate the 3D position of communication sources, identify trusted senders, and reject unverified transmissions. This capability makes it highly effective for secure satellite networks, defense applications, and high-speed optical data transfer.
By leveraging neuromorphic vision sensors and neuromorphic processors, this system enables fast, low-latency optical communication, improving the robustness and security of satellite-to-satellite and satellite-to-ground links. The approach is particularly advantageous for autonomous tracking, space-based mesh networks, and high-speed optical data relays in dynamic environments.
This diagram (FIG. 3) illustrates a free-space optical (FSO) communication network utilizing neuromorphic vision sensors and neuromorphic processors for high-speed optical data transmission. The system consists of multiple communication nodes, including satellites (302a, 302b), a ground station (306), an aerial platform (304), and a vehicle-based receiver (308).
Each of these nodes is equipped with an optical communication system (310) that includes neuromorphic cameras for detecting and processing optical signals. The diagram demonstrates how optical signals are exchanged between satellites and ground-based receivers, forming a space-based optical mesh network. The neuromorphic vision sensors in the system enable real-time processing of light signals by detecting changes in brightness at high speeds, reducing latency and improving communication reliability.
This system is designed for secure, high-bandwidth, low-latency optical communications, particularly for applications in satellite networks, aerospace, defense, and autonomous vehicle communication.
US20210348966 - Systems, devices, and methods for hyperspectral imaging
https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=US341179803
This patent describes a hyperspectral imaging system that integrates neuromorphic vision sensors with an interferometer to capture and process spectral data in real-time across visible and non-visible wavelengths (e.g., infrared and ultraviolet). The system uses an event-based neuromorphic camera, which detects brightness changes asynchronously at each pixel, significantly reducing data redundancy and improving response time compared to conventional imaging. Light from an interferometer, such as a Translating Wedge-Based Identical Pulses Encoding System (TWINS), is processed by a neuromorphic processor that applies digital demodulation and a Non-Uniform Discrete Cosine Transform (NDCT) to extract spectral information. This enables the generation of hyperspectral images with precise spectral resolution, suitable for military surveillance, medical diagnostics, remote sensing, and security applications. The system also includes a calibration laser for spectral accuracy and adaptive processing that dynamically adjusts spectral bands in response to real-time conditions. By leveraging neuromorphic processors and neuromorphic vision sensors, this technology provides high-speed, low-latency spectral analysis with enhanced sensitivity in low-light environments, making it ideal for applications requiring real-time hyperspectral imaging and advanced object detection.
This diagram illustrates a hyperspectral imaging system that integrates an interferometer, neuromorphic vision sensor, and event-based processing for real-time spectral analysis. Light from an input scene passes through a Translating-Wedge-Based Identical Pulses Encoding System (TWINS) interferometer, modulated by a resonant actuator and calibrated using a laser source. The processed light is captured by a neuromorphic event camera, which detects brightness changes asynchronously and outputs an event stream instead of conventional frames. This stream is processed by a neuromorphic processor that applies digital demodulation and frequency transforms to extract spectral data, generating hyperspectral images with enhanced resolution and sensitivity, ideal for applications like remote sensing, medical imaging, and defense.
ChatGPT description of these individual components forming part of a missile defense system:
This system would be an advanced real-time detection, tracking, and interception network designed to counter hypersonic missiles, stealth aircraft, and other high-speed threats. It combines neuromorphic vision sensors, hyperspectral imaging, optical communication, and AI-powered 3D reconstruction to create a fast, power-efficient, and highly adaptive defense system.
How It Works:
Detection & Early Warning
- Neuromorphic sensors detect light and movement instantly, even in total darkness or bad weather.
- Hyperspectral imaging identifies missile exhaust plumes, stealth coatings, and heat signatures that evade traditional radar.
- Event-based cameras only process changes in the scene, reducing data overload and making response times faster
Tracking High-Speed Threats:
- 3D reconstruction builds a real-time model of the target’s movement using multiple sensors.
- AI-enhanced neural radiance fields (NeRFs) predict the missile’s flight path, even if it maneuvers unpredictably.
- Infrared and neuromorphic fusion allows tracking without relying on radio signals that can be jammed.
Interception & Countermeasures:
- Optical communication networks link satellites, drones, and ground-based interceptors for ultra-fast coordination.
- Adaptive targeting algorithms adjust intercept trajectories in milliseconds to counter evasive maneuvers.
- Low-latency AI processing ensures that defenses respond before traditional missile defense systems can react.
Why It’s a Game-Changer:
- Defeats Hypersonic Threats: Traditional radars struggle with Mach 5+ speeds and unpredictable flight paths—this system doesn’t.
- Works in Any Environment: Optical and event-based sensors see through clouds, electronic warfare, and stealth technology.
- Faster Decision-Making: AI-powered neuromorphic processing reduces reaction time to near-instantaneous.
- Networked Defense: Satellites, drones, and ground systems communicate instantly without radio jamming vulnerabilities.